Honduras is immersed in an action plan to promote sustainable economic growth that positively impacts its commitments to citizens, the improvement of strategic infrastructure and the increase of resilience to climate change.
The region’s economic development suffered a tough setback during the pandemic, especially in 2020, when it had just begun an incentive reactivation plan to attract investment. The macroeconomic results revealed by the Central Bank of Honduras (BCH) reflect that economic activity has been strong during 2023, showing the country’s resilience to internal and external vicissitudes and uncertainties.
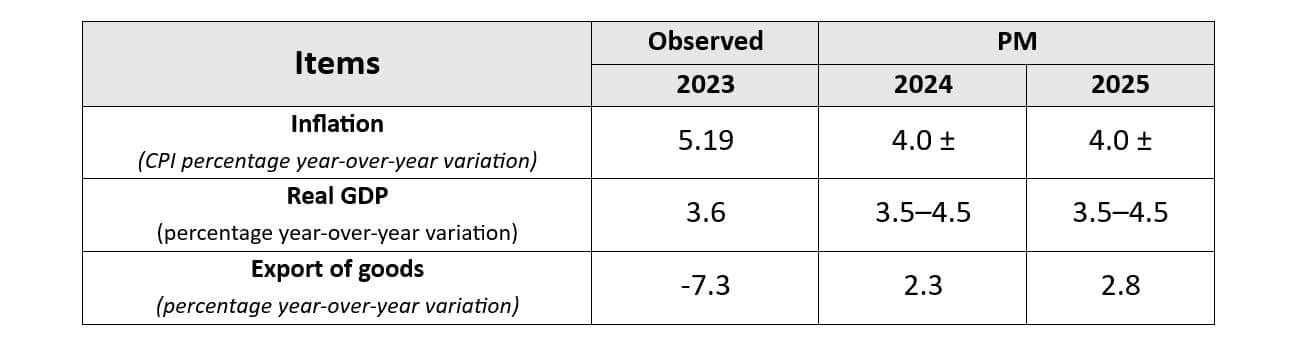
In this sense, the real GDP in Honduras grew by 3% in the first quarter of 2023, compared to 2022, starting the year with good prospects despite negative factors such as the impact of the El Niño phenomenon, which especially impacted agricultural activity, or the decrease in external demand of the main commercial partners. Year-end economic growth reached 3.6%, down 0.9% from the previous year. Even with all that, and as reflected in a report from the National Autonomous University of Honduras, the outlook for 2024 and 2025 is slightly more encouraging, with the estimate being between 3.5% and 4.5%.
Sustaining Inflation
Inflation has managed to stay under control since 2022 thanks to the restrictive monetary policies applied by the BCH. The year-on-year rate, as of the end of 2023, was the lowest rate in three years (5.19%), as a result of lower fuel prices, the electric rate and lower growth for certain food prices. These values were also influenced by evolving raw material and oil costs. For 2024, a downward trend is expected, within the medium-term tolerance range established by the BCH (4%±) at the end of 2024 and 2025, at the same time international food and fuel prices are being contained. The table below shows the most recent results and future prospects.
An economy based on the tertiary sector
We looked at the latest report on the region published by ICEX (Instituto Español de Comercio Exterior [Spanish Institute for Foreign Trade]) in December 2023 to discover that the tertiary sector is the most important in its economy, employing 44.4% of the active population and representing 65.6% of GDP.
Honduras is a growing tourist destination, boasting attractions such as beaches and islands surrounded by the world’s second-largest coral barrier, diverse ecological reserves, indigenous cultures, Mayan archaeology and colonial cities.
The second sector that contributes the most to Honduran GDP is the secondary sector. The manufacturing industry, which adheres 19.5%, is divided into three distinct sub-sectors.
- The traditional industry, which provides processed foods, beverages and clothing for the domestic dairy market.
- The processing industry, related to the main agri-export products dominated by the U.S. multinational companies Chiquita and Dole and supplying both the local market and the foreign market.
- Textile manufacturing, whose development began in the 1990s. Since then, more than 250 companies have established themselves in the country in the 25 existing industrial parks.
Finally, the primary sector employs 36.6% of the active population and represents 12.2% of GDP.
Poor energy sources
According to the ICEX report, the region lacks its own energy resources, except for electrical generation of hydraulic and photovoltaic origin. About half of the supply comes from imported oil. All things considered, the country aims to have an energy matrix in which renewable sources prevail, for which various projects have been implemented within the country.
In 2013, the Law for the Promotion of Electric Power Generation with Renewable Resources was reformed, and a 10% incentive was established on the base price and extensive exemptions for these projects. These advantages led to the installation of almost 500MW of solar photovoltaic energy, mainly in the southern part of the country, starting the following year, and difficulties are being faced with its integration given the limited planning of the government.
The National Electric Power Company (ENEE) is responsible for the distribution and practically all of the hydroelectric generation and a portion of the thermal generation, while the bulk of the thermal generation has been contracted with private companies.
A push to Direct Foreign Investment
In Honduras, foreign direct investment (FDI) is regulated through the Investment Promotion and Protection Act of 2011 and its 2014 regulation. They receive the same treatment as locals and try to facilitate and guarantee the entry of investment, both domestic and foreign.
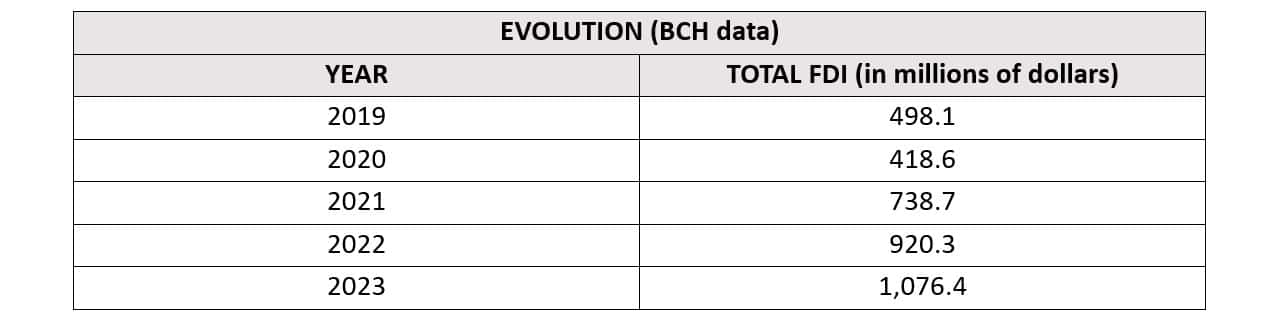
FDI has grown considerably over the last five years; from 2019 to 2023, the total increase has exceeded 73%. The main receiving sectors in the last fiscal year have been:
- Transformational Goods Industry – Textile manufacturing ($473 million)
- Services ($463.1 million)
- Electricity, Gas and Water ($79.5 million)
- Commerce, Restaurants and Hotels ($73.6 million)
- Transportation, Storage and Telecommunications ($63.2 million).




